Introduction: The Iron Ore Market in a Changing World
The global iron ore market stands as one of the key pillars of modern industry, underpinning the steel production that builds everything from skyscrapers and railways to automobiles and renewable energy structures. In today’s rapidly evolving economic environment, a combination of robust growth drivers, environmental challenges, and geopolitical tensions creates a market that is both promising and wrapped in tricky parts. As we take a closer look into the inherent qualities and current trends of the iron ore market, we uncover a landscape marked by practical opportunities and intimidating challenges alike.
Global Iron Ore Market Dynamics and Forecast
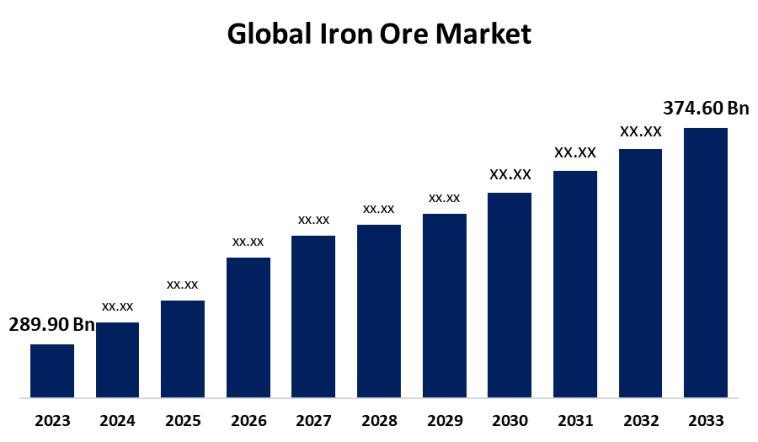
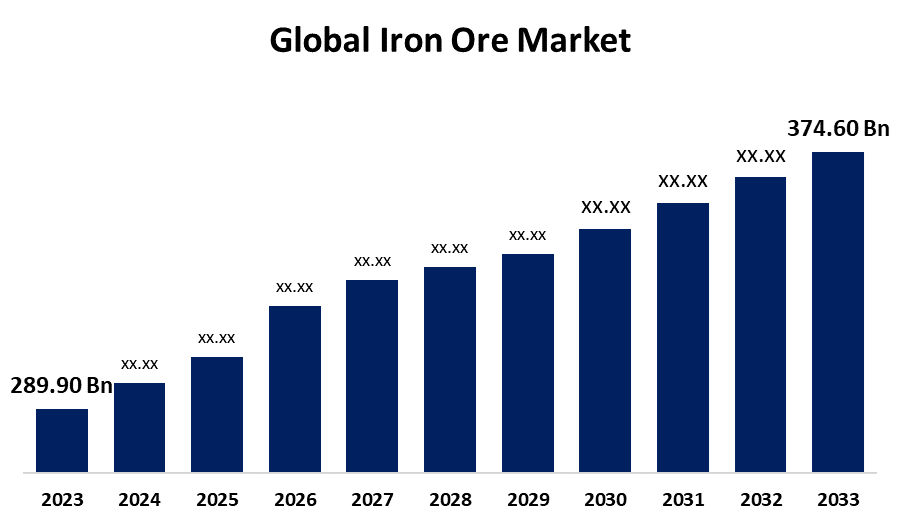
Valued at approximately USD 288.26 billion in 2024, the iron ore market is projected to climb to about USD 299.73 billion by 2025 and further escalate to nearly USD 409.57 billion by 2033. This growth, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 3.98% from 2025 to 2033, underscores the market’s resilience and indicates sustained demand for the resource essential to steel production – which accounts for over 98% of global usage.
Understanding Iron Ore Grades: Hematite Versus Magnetite
Iron ore is primarily classified by grade, with high-grade ores preferred in modern industrial applications. Hematite and magnetite emerge as the two key varieties in this discussion. Hematite, typically containing 60–66% iron, is prized for its high iron content and reduced processing requirements. In contrast, magnetite ores, although historically considered less desirable due to their lower initial grade, are steadily gaining attention as technological improvements in beneficiation make their processing more energy-efficient.
A closer look at these segments not only highlights the fine points that differentiate them, but also the subtle differences in extraction techniques, production costs, and energy implications. For instance, the hematite segment is the backbone of traditional blast furnace operations, providing a nearly turnkey solution for high-yield steelmaking. Magnetite, meanwhile, is becoming increasingly popular in direct reduced iron (DRI) processes as industries worldwide move toward low-emission operations.
| Ore Type | Iron Content (%) | Primary Use | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematite | 60 – 66 | Traditional Blast Furnaces | High purity and lower processing costs |
| Magnetite | 25 – 35 (raw) / up to 68 (beneficiated) | DRI and Emerging Technologies | Cost-effective refining with modern techniques |
The table above serves as a quick guide through the subtle parts involved when comparing hematite and magnetite, highlighting the practical differences that affect overall production and sustainability milestones.
Environmental Impact, Carbon Emissions, and the Decarbonization Debate
A critical facet of the iron ore market revolves around its role in generating carbon emissions. Steel production alone is responsible for about 7% of global direct CO₂ emissions, a statistic that places heavy industry in the eye of decarbonization debates. As governments and companies strive to reduce their carbon footprints, the environmental impact of mining operations has become both a concern and a catalyst for innovation.
The shift toward sustainable practices has spurred interest in low-carbon steel production methods, such as hydrogen-based reduction processes and natural gas-driven direct reduction plants. These emerging technologies represent game-changing opportunities but also bring a set of tricky parts associated with upgrading legacy production systems. For the iron ore industry, the challenge is twofold: meeting the immediate global demand for steel while transitioning to cost-effective low-emission production techniques.
Urban Infrastructure and Industrial Demand in the Iron Ore Market
Rapid urbanization and accelerated infrastructure projects in emerging economies are acting as super important growth drivers for the iron ore market. As nations across Asia, Africa, and Latin America witness dramatic expansion of urban centers, the demand for structural steel surges, inevitably elevating the spotlight on iron ore as the foundational raw material for such projects.
Emerging Economies and Rapid Urbanization
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs forecasts that more than 2.5 billion people will be added to urban populations in developing nations by 2050. This swell in urban populations directly fuels the need for modern infrastructure, from railways to metro systems and from highways to residential developments. In India alone, the National Infrastructure Pipeline outlines a planned spending of over USD 1.3 trillion through 2030. With an annual rise expected at around 6.8% in steel demand for transportation projects, it is clear that increased urbanization is setting a positive backdrop for rising iron ore consumption.
Infrastructure booms in these developing regions ensure that the market remains robust, even as the industry faces other headwinds. In essence, the expansion in urban areas ties directly into the iron ore cycle, reflecting an ever-growing reliance on the resource – not only for construction needs but also as a key contributor to the overall modernization of an economy.
China’s Dominant Role in the Global Iron Ore Economy
No discussion of the iron ore market would be complete without acknowledging the gargantuan influence of China. As the world’s largest consumer of iron ore, China’s appetite and import dependency largely dictate market conditions. With domestic ore often averaging less than 35% in iron content, Chinese steel mills are compelled to import high-grade ore to meet production requirements. The Port of Qingdao, recognized as the largest iron ore terminal in the world, handled over 150 million tonnes in 2023 alone. Such scale ensures that any fluctuations in Chinese steel production send ripple effects throughout the global market.
China’s quagmire in sourcing the right grade of ore ultimately acts as both an opportunity for international exporters and a nerve-racking dependency highlighting potential vulnerabilities in the metal supply chain. This reliance underscores how central Chinese steel production is to the evaluation of global prices and trade flows in iron ore, making it a key focal point for analysts and investors alike.
The Environmental and Regulatory Hurdles Facing the Iron Ore Industry
While the iron ore market is ripe with opportunities, it is also wracked with a series of problematic environmental challenges and regulatory twists and turns. As stakeholders grapple with the ecological impact of mining, the industry is under increasing scrutiny from regulators and civil society groups globally.
Declining Ore Quality and the Resulting Cost Implications
One of the notable challenges confronting the industry is the gradual deterioration in ore quality. Lower-than-expected iron content in mined ore translates into more energy-demanding processing, which, in turn, leads to escalated production costs and a larger volume of waste materials. For example, data from the Pilbara region in Australia indicate that the average hematite grade has dropped from 62% Fe in 2010 to about 58.5% Fe in 2023.
Such trends have the following consequences:
- Increased Beneficiation Needs: Lower-grade ores require additional processing steps, resulting in higher consumption of energy and water.
- Higher Environmental Footprint: More processing means more tailings and waste, contributing to environmental degradation.
- Higher Operational Costs: The economic feasibility of mining projects is challenged when ore quality declines, forcing companies to invest in advanced technology and mitigation measures.
These worrying figures serve as a reminder that while the market may be expanding, the underlying geological challenges require a concerted effort to find your way through technological upgrades and strategic shifts in processing protocols.
Environmental and Regulatory Pressures on Mining Operations
The modern mining landscape is increasingly defined by off-putting environmental compliance standards and regulatory constraints. Many mining practices come with a legacy of water contamination, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions. The high-profile failure of the Vale Córrego do Feijão tailings dam in Brazil in 2020, which tragically resulted in a significant loss of life, has catalyzed a global movement toward stricter audit protocols and real-time monitoring of tailings facilities.
Furthermore, initiatives like the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive impose substantial cost pressures on mining operations, mandating substantial reductions in sulfur and particulate emissions. These regulatory efforts, while essential for environmental conservation, add layers of complicated pieces that mining companies must manage in addition to fluctuating market demands.
Opportunities Amid the Challenges: Advancements and Renewed Focus on Technology
Despite the nerve-racking concerns regarding environmental impact and declining ore quality, the iron ore market is simultaneously brimming with fresh possibilities. Technological progress has unlocked new opportunities that promise to redefine the industry’s landscape in the coming years.
Rising Adoption of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) and Alternative Steelmaking Technologies
One of the most promising avenues to alleviate environmental burdens while sustaining growth in iron ore demand is the rise of natural gas-based and hydrogen-ready direct reduced iron technologies. DRI processes, which rely on the direct method of reducing iron ore, have been gaining ground globally. In 2023, DRI production accounted for approximately 76 million tonnes – a figure that is anticipated to grow as industries seek cleaner and more efficient solutions.
For instance, in Oman, the National Iron and Steel Company (NISCO) operates one of the world’s largest DRI plants, underlining the market potential when you steer through emerging alternatives. With the environmental advantage of lower CO₂ emissions, adoption of DRI not only mitigates some of the environmental criticisms but also paves the way for cost-effective and scalable production, offering a promising alternative to traditional blast furnace routes.
Infrastructure Investments: Modernizing Rail and Port Systems to Reduce Logistics Bottlenecks
In addition to technological innovations, significant investments in infrastructure are actively addressing the complicated pieces of logistics that have long hampered the iron ore market. Enhancements in rail and port infrastructure can dramatically lower transportation costs and connect remote mining areas with global markets more efficiently.
A prominent example of this trend is the Roy Hill project in Western Australia. The project recently completed a 344-kilometer rail line and a dedicated port terminal, which has substantially boosted the annual transportation capacity – facilitating the movement of about 55 million tonnes of iron ore. Infrastructure projects like this are not only reducing transportation delays but are also reinforcing the overall competitiveness of the market by streamlining the supply chain.
Geopolitical Concerns and Supply Chain Challenges
Beyond the operational and technological challenges lie the broader, nerve-racking aspects of geopolitical tensions and fragmented supply chains. As the iron ore market is deeply enmeshed in global trade, any disruptions in political stability or international relations can have immediate and widespread effects.
Vulnerability to Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Restrictions
Recent years have demonstrated that global trade in iron ore is delicately balanced and can be thrown off by geopolitical events. Sanctions on major producing nations, such as the sanctions imposed on Russia, have influenced trade routes and led to elevated maritime insurance premiums – a jump of about 22% in some sensitive areas in 2023. These shifts not only impose extra costs, but also create an atmosphere loaded with issues that can ripple across the market.
Other regions, including Indonesia, have also implemented export restrictions to protect domestic resources. Such measures exacerbate concerns over future supply security and underline the importance of developing diversified supply chains and exploring local efficiencies wherever possible.
Managing the Operational Challenges in Remote and Harsh Environments
The extraction of iron ore naturally involves working through some of the more intimidating operational environments. Many of the world’s richest iron ore deposits are located in remote regions characterized by severe weather conditions and extreme climates. For example, in Australia’s Pilbara region, operating temperatures often soar above 45°C, contributing to increased absenteeism and reduced worker productivity. Similarly, in northern Quebec, prolonged winters and icy conditions can delay exploration and transport schedules, with up to 30% of annual rail operations being affected by winter conditions.
These challenging environments require mining firms to innovate and invest in specialized equipment and practices. Strategies such as enhanced weather forecasting systems, automation, and digital twin technologies are being deployed to figure a path through these tricky parts of operational logistics, ensuring that production remains as continuous and efficient as possible.
Competition Landscape and Strategic Maneuvering Among Industry Titans
The iron ore market is characterized by a concentrated oligopoly dominated by multinational giants whose decisions shape global trade flows and pricing standards. As the market evolves, companies are increasingly focusing on more than just volume and cost leadership – they are aiming to differentiate themselves through sustainability, product purity, and digital integration.
Industry Leaders and Their Market Strategies
Some of the major players steering the direction of the iron ore market include Vale S.A., Rio Tinto, BHP, Fortescue Metals Group, and Anglo American plc, among others. These companies are adapting to both old and new challenges by:
- Investing in Automation and Digitalization: Utilizing technologies like autonomous haulage systems, real-time ore monitoring, and digital twin simulations to optimize extraction efficiency.
- Emphasizing Sustainability Initiatives: Launching projects focused on reducing carbon footprints, such as low-carbon pellet development and renewable-powered mining operations.
- Focusing on High-Grade Outputs: Prioritizing the production of high-grade iron ore to meet the demands of modern, energy-efficient steelmaking processes.
Examples in practice include Rio Tinto’s Gudai-Darri mine in Western Australia – touted as one of the most technologically advanced iron ore operations globally – and BHP’s significant investments in digital blending solutions and decarbonization strategies. These measures not only enhance operational efficiency but also build resilience against the challenging economic and environmental factors influencing the market.
Shifts in Competitive Dynamics and the Importance of Sustainability
The influence of sustainability on market competition has been profound. Leading companies are now shifting their focus from simply maximizing output to integrating eco-friendly practices that bolster their long-term relevance. For instance, Vale S.A. has rolled out its Green Pellets initiative, designed specifically to supply low-emission iron ore to Asian steel manufacturers. Through real-time digital quality data, buyers can now customize ore specifications, making the entire supply chain more adaptable and responsive.
This shift toward greener practices is not purely symbolic – it is a necessary evolution. As environmental regulations tighten and public pressure mounts for reduced industrial emissions, companies that are able to figure a path toward sustainable operations stand to gain a competitive edge. In this context, the balance between production efficiency and meeting environmental standards represents one of the little twists that will likely shape the industry’s future trajectory.
Future Trends: Technological Innovation and Evolving Market Demands
The iron ore market of tomorrow will be distinguished by a convergence of deep technological innovation, evolving consumer attitudes, and regulatory pressures that demand operational excellence. With the pressing need to reduce CO₂ emissions, companies are increasingly exploring cutting-edge solutions such as hydrogen-based reduction and next-generation beneficiation processes.
Moreover, emerging trends in automation and digital integration are poised to revolutionize the way mining is conducted. Predictive maintenance, artificial intelligence, and smart logistics are becoming indispensable to manage the twists and turns of modern ore extraction. Companies that embrace these advanced technologies not only mitigate many of the confusing bits of traditional methods but also enhance safety, reduce operational costs, and improve overall efficiency in what remains a highly competitive global market.
Digital Transformation in Mining Operations
The digital transformation sweeping across industries has not spared mining. Today’s technological advancements allow companies to integrate digital twin technologies with automation systems to create highly streamlined operations. Key benefits include:
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing sensors and real-time data to anticipate equipment failures, thus avoiding costly downtime.
- Enhanced Safety Protocols: Monitoring working conditions continuously to protect workers from the extreme climates of remote mining locations.
- Optimized Production Schedules: Adjusting operations dynamically based on demand forecasts and logistical conditions.
Such strategies not only help companies reduce production expenses but are also super important in maintaining competitiveness against a backdrop of increasing production costs and intense market competition.
The Evolution of Steel Production Techniques
The next decade is likely to witness a gradual but significant shift in steel production techniques, driven by environmental concerns and the need for efficient resource use. Traditional blast furnace operations may gradually give way to alternative routes like DRI and hydrogen-based reduction, which significantly reduce emissions and energy usage. This evolution is likely to transform not just the iron ore market but the entire steel value chain, enabling a smoother transition toward a more sustainable industrial paradigm.
Final Thoughts: Charting a Responsible Path Forward
In conclusion, the global iron ore market, with its enormous value and critical role in modern construction and industrial growth, faces a future filled with both enormous opportunities and significant challenges. As emerging markets pump up urban infrastructure and companies worldwide brainstorm greener production techniques, the market’s inherent potential continues to shine even amid a series of tricky parts – ranging from diminishing ore grades and escalating processing costs to geopolitical tensions and environmental compliance demands.
Stakeholders must take a closer look at how investments in technology, infrastructure, and sustainability can carve out a more resilient market framework, ensuring that the transition toward low-carbon steel production remains smooth. Companies that manage to reason through the tangled issues of environmental responsibility, operational efficiency, and geopolitical risk will likely thrive, setting the stage for continued growth over the coming decade.
For policymakers, investors, and industry participants, the core challenge lies in steering through the operational twists and turns while making sure that modern iron ore extraction and processing become both economically viable and environmentally sound. Whether it is by embracing digital innovations, investing in sustainable technologies, or refining supply chains against the backdrop of global trade uncertainties, the path forward demands flexibility, foresight, and a balanced approach to risk and opportunity.
As we look to the future, the journey of the iron ore market serves as a fascinating microcosm of today’s complex industrial landscape—marked by impressive growth potential, significant risks, and the need for smart, resilient solutions. In this dynamic and evolving space, charting a responsible path forward will require all players to work together, invest in the right technologies, and remain adaptable in the face of unpredictable global trends.
Ultimately, the iron ore market is much more than just a commodity—it’s a critical component of our modern economic and industrial fabric. By taking a proactive and innovative approach that balances economic demand with environmental necessity, the industry can continue to lay the groundwork for our future infrastructure, ensuring that progress does not come at the expense of sustainability and responsible resource management.
This opinion editorial has sought to take you on a journey through the many layers of the iron ore market, highlighting everything from grade differences and technological shifts to regulatory challenges and global market dynamics. It is an invitation to dig into the reality of a sector that, despite its age-old legacy, is continuously reinventing itself in response to modern challenges and opportunities. By understanding the fine points, little details, and subtle differences across the spectrum of iron ore production and trade, stakeholders can better equip themselves to find their way through this ever-changing landscape.
In the end, while the path ahead may be filled with nerve-racking challenges and confusing bits, the resolute drive toward modernizing operations and embracing sustainable practices offers a hopeful outlook for the industry and its vital role in supporting global progress.
Originally Post From https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/iron-ore-market
Read more about this topic at
Global iron ore market: 2025 outlook
Iron ore to play key role in a decarbonized future