An Opinion on the Expansion of 50% Tariffs on Steel and Aluminum Products
The recent decision by the US Department of Commerce to expand the 50% tariffs on steel and aluminum to an additional 407 products marks a significant turn in US trade policy. As an observer of economic trends and policies, I find it important to take a closer look at this change, exploring both the immediate and longer term impacts on multiple sectors such as industrial manufacturing, automotive, energy, and even small businesses. In this article, we will dive in to get into the details, scrutinize the tricky parts of these trade measures, and discuss the tangled issues that may arise from their implementation.
Expanding the Scope of Tariffs: A Detailed Overview
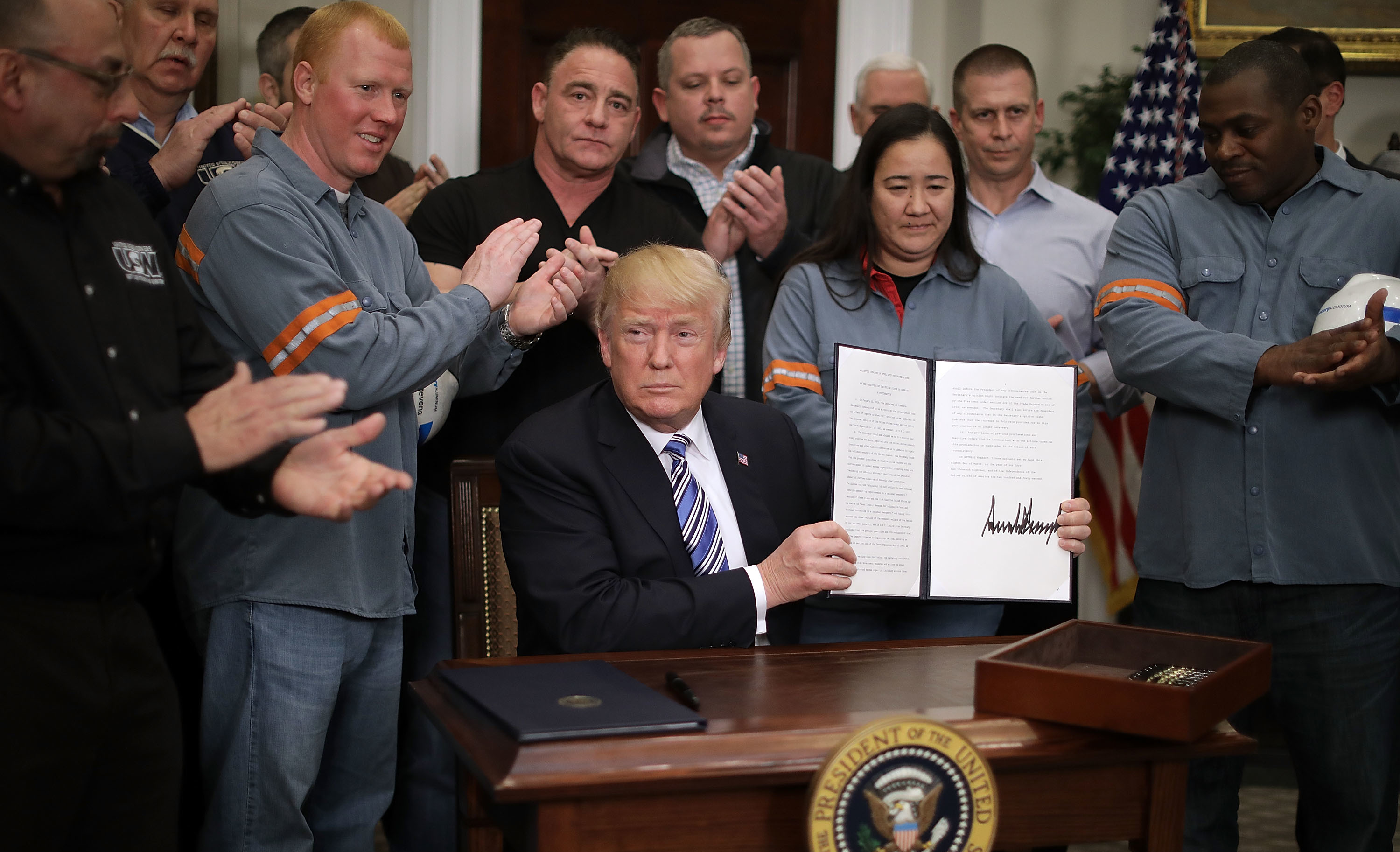
On August 18, following a brief window of anticipation, the new tariff rules took effect. Originally imposed by President Donald Trump earlier this year, the 50% tariff regime was aimed at protecting the national interests of US steel and aluminum producers. By extending these tariffs to include about 407 more products – ranging from baby chairs to wind turbines, railcars, furniture, heavy machinery, and compressors – the government intends to fortify domestic industries and prevent potential loopholes that might have been used to evade the tariff system.
Jeffrey Kessler, the US Under Secretary of Commerce for Industry and Security, stressed that the new measure is designed to close gaps for tariff evasion and support the national manufacturing base. However, the expansion has also sparked debate among stakeholders who contend that such measures may have unintended consequences for both US and global trade.
The Broader Implications for US Industry and Global Trade
The expansion of tariffs has far-reaching consequences across various economic sectors. While the intent is to protect US industries—especially those related to steel and aluminum production—the broader implications extend to sectors like automotive, industrial manufacturing, and even energy infrastructures. Critics argue that while the immediate goal might be to secure domestic production, the long-term effects could include increased costs for manufacturers who rely on these materials for their production processes.
Below are some key areas where the extended tariffs may have notable effects:
- Automotive Sector: Increased costs for components, leading to redesign budgets and potential price hikes for consumers.
- Industrial Manufacturing: The supply chain faces obstacles as previously cost-effective imports now become more expensive, forcing companies to either absorb the new costs or pass them to consumers.
- Energy and Infrastructure: Components used in building and infrastructure projects such as wind turbines and heavy machinery might result in additional expenses, which could delay project timelines.
- Small Businesses: Particularly those in sectors like home manufacturing furniture or even baby products may see price increases, risking consumer demand and reducing competitiveness.
Analyzing the Tricky Parts of Tariff Policy Expansion
The move to extend tariffs can be seen as a double-edged sword from a policymaker’s perspective. On one hand, critics argue that the measure is a tactical step to shield domestic industries from what is perceived as unfair foreign competition. On the other, detractors warn that the consequence of such actions might be a ripple effect across multiple layers of the economy, touching inconsistent bits of industrial activity that are interdependent.
To better understand these tricky parts, let’s figure a path through the following considerations:
- Competitive Pressure: Domestic companies may not be fully prepared to cope with sudden cost increases, placing them in a comparatively disadvantaged position against competitors in other countries not facing similar tariffs.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The extended tariffs can cause supply chain headaches and force companies to either source more expensive substitutes or reconfigure their production processes entirely.
- Market Dynamics: As companies adjust to pass on the extra costs to consumers, there might be upward pressure on prices. This kicking-in effect might ultimately dampen demand—especially in sectors sensitive to price shifts like the automotive market.
Impact on Industrial Manufacturing and Automotive Sectors
Industrial manufacturing and the automotive sector are particularly vulnerable to such changes. Products that rely heavily on steel and aluminum can quickly see production costs escalate. For instance, manufacturers of railcars, heavy machinery, and even furniture might find themselves grappling with higher input costs, prompting them to either lower profit margins or risk market traction by passing costs on to customers.
This shift can be especially nerve-racking for industries that struggle with traditional cost pressures. As supply chains are forced to either absorb the extra expense or incorporate it into final pricing, the consequences are multifold:
- Increased production costs affecting profitability and potentially leading to lower capital reinvestment in new technologies and process improvements.
- Pressure on consumer spending as prices soar on end products, which might slow down the pace of growth in consumer-driven sectors such as automobile sales and home furnishings.
- The potential for trade disputes as international partners look to retaliate or re-align their own trade policies in response to such barriers.
Assessing the Ripple Effects for the Global Supply Chain
When governments impose tariffs, especially on products that form the backbone of various industries, it is often a sign that the ring is too big to ignore. The global supply chain, already contorted by previous political and economic twists and turns, now faces additional hurdles. Trading partners like the European Union, Japan, and others could see these measures as off-putting and might respond with their own trade barriers.
Some stakeholders predict that these actions may prompt a realignment of trade agreements and even lead to lengthy disputes on platforms like the World Trade Organization (WTO). The following points highlight some of the global challenges that may follow:
-
Trade Retaliation:
- Foreign nations may introduce their own retaliatory tariffs on key US exports such as agricultural goods, automotive products, or technology, further complicating trade relations.
- This back-and-forth exchange can create a tense environment in international negotiations, potentially delaying the signing of new agreements or even destabilizing existing partnerships.
-
Investment Uncertainty:
- Foreign investors might be put off by an environment that seems loaded with problems, prompting them to look for more stable markets.
- Inconsistent trade policies can result in a situation where business confidence is eroded, leading to delays in capital investments.
-
Innovation and Technology:
- The disruption of free trade flows might set back collaborations in technology and research, particularly in sectors where innovation depends on the international exchange of ideas.
- Strained supply chains can hinder access to raw materials necessary for research and development.
The Effects of Tariff Expansion on Small Businesses and the Economy
Small businesses are the lifeblood of the American economy, yet they are perhaps the most vulnerable when it comes to policy shocks such as a sudden tariff hike. Many small enterprises operate on tight margins and rely on steady supply chains that may become overwhelmed by these new, complicated pieces of legislation. Rising input costs and supply challenges threaten not only the balance sheets of these businesses but also the overall competitiveness of their offerings.
Consider the following factors as small businesses strive to get around these newly imposed restrictions:
-
Cost Absorption:
Some companies may have to absorb the additional costs in the short term, risking profit margins that have already been squeezed by inflation and rising operational expenses.
-
Price Pass-Through:
Other businesses might opt to pass these costs onto consumers. While this could help maintain margins, it might also reduce demand, particularly in a market where price sensitivity is a critical concern.
-
Resource Reallocation:
Companies may need to reconfigure their resources by sourcing alternative materials that are not subjected to these tariffs, or by innovating new products that minimize the use of steel and aluminum. Both choices involve off-putting investments in research and development as well as a period of adjustment that could slow down production.
Interestingly, the extended tariffs might also have mixed effects on domestic production. While it may stimulate production in industries that rely on domestically sourced raw materials, the overall cost structure for small businesses remains a major struggle. The tension between protecting domestic industries and ensuring affordable market prices is a classic case of policy trade-offs that policymakers need to address sensitively.
What Do Industry Leaders Say?
Industry experts have weighed in on the potential consequences of expanding tariffs on steel and aluminum products. While many agree that the steps taken to close loopholes are necessary for the integrity of national industrial policy, there is widespread concern that the broader policy might have unintended effects on global trade relationships and domestic production costs.
Some industry leaders point out that the tariffs could be a double-edged sword:
- Proponents’ Viewpoint: Advocates for the tariffs argue that the move is essential to curb unfair practices and to ensure that American producers face a level playing field. They believe that by blocking avenues for tariff evasion, the move could shield local industries from excessive foreign competition.
- Critics’ Perspective: On the flip side, critics are worried that this approach is too simplistic. They note that the economic landscape is full of tricky parts—ranging from increased production costs to potential trade wars that might leave more problems than solutions.
The divergent views remind us that trade policy, much like any economic instrument, carries the weight of both immediate benefit and long-term burden. Industry leaders call for a balanced approach where the forces of protection and free trade are carefully weighed.
Managing Your Way Through the Economic Twists and Turns
It is essential that policymakers, business leaders, and the international community work together to find a path that minimizes the negative ripple effects of these tariff expansions. The economic environment remains on edge as companies figure a path through rising costs, supply chain reconfigurations, and potential trade disputes.
Dealing with such sweeping measures involves careful planning and an acute awareness of the slight differences in how various sectors absorb and translate increased costs. Here are some strategic approaches companies may consider:
-
Supply Chain Diversification:
Businesses might need to diversify their sources of raw materials and components. This strategy is not without its own set of challenges, as finding alternative suppliers that match the quality and cost-effectiveness of imported goods can be nerve-racking.
-
Process Innovation:
The pressure of increased tariffs often spurs innovation. Some companies could use this as an impetus to re-engineer their production methods, thereby reducing reliance on materials subject to these heavy tariffs.
-
Pricing Strategy Adjustment:
Businesses may also explore innovative pricing models that adjust more fluidly to economic changes, sharing some of the increased costs with consumers gradually rather than abruptly.
Realigning Strategies in an Era of Policy Change
Small businesses and larger manufacturers alike must consider the following steps to manage the effects of these tariffs without losing market traction:
| Strategy | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Diversification |
|
|
| Process Innovation |
|
|
| Pricing Strategy Adjustment |
|
|
Economic Perspectives and Policy Options
From an economic standpoint, the extended tariffs represent both an opportunity and a challenge. While the move aims to secure critical domestic industries, it also risks creating an environment that is full of problems for investors and small businesses alike. Trade policies that are off-putting to business investment can, over time, undermine the overall competitiveness of an economy that is already dealing with global competition.
Policymakers are now tasked with reconciling two seemingly opposing priorities:
-
Protectionism vs. Global Trade Integration:
There is an essential need to protect domestic industries while also encouraging a trade environment that is conducive to international partnerships. In balancing these priorities, the government must keep in mind the hidden complexities of global supply chains and the slight differences between industries.
-
Short-term Gains vs. Long-term Stability:
Efforts to immediately bolster domestic production might inadvertently lead to long-term economic uncertainty. Ensuring that long-term goals are not lost in the rush to address immediate challenges is critical in crafting sustainable industrial policies.
One promising path is to engage in multilateral dialogues that can help find a middle ground. The benefits of such an approach include:
- Enhanced international cooperation to address shared challenges within the industry sectors impacted by tariffs.
- Opportunities for establishing bilateral and multilateral agreements that reduce the need for punitive measures while still safeguarding domestic industry interests.
- Policy frameworks that encourage collaboration on technology, research, and innovation initiatives across borders.
Lessons from Past Policy Shifts
History shows us that major trade policy shifts are often accompanied by adjustment periods for businesses, both large and small. In previous instances when the US or other major economies intervened in the market with protective measures, there was invariably a period when companies had to scrape through the confusing bits of new regulatory and supply chain requirements.
Looking back can provide valuable insights:
-
Historical Precedents:
Earlier tariff increases, whether in the steel industry or other sectors, demonstrated that while initial market shocks may appear overwhelming, businesses eventually adapt. The key is a flexible approach that accounts for both the larger industry trends and those tricky parts of the process that might be overlooked initially.
-
Adjustment Strategies:
Industries that invested in supply chain innovation and diversified their markets managed to weather the storm more effectively. Those companies that looked for creative internal restructuring avoided having to completely overhaul operations.
The Road Ahead: What Can Businesses and Policymakers Do?
It is clear that the expansion of these tariffs is not a decision made lightly, nor is it without controversy. For businesses, the challenge will be managing your way through these new pricing pressures and supply chain adjustments while remaining competitive. For policymakers, the task is to ensure that protecting US industry does not result in long-term economic strain.
Key measures moving forward may include:
-
Enhanced Transparency:
Providing clearer guidelines on how tariff-related costs are calculated and informing affected industries about the timeline for potential changes can help companies take more precise action when planning budgets and operations.
-
Regular Policy Reviews:
Frequent reviews and adjustments of tariff policies can help address the evolving nature of global supply chains. This adaptable approach allows policymakers to tweak measures to reduce the risk of trade disputes while ensuring that domestic industries remain competitive.
-
Support Programs for Small Businesses:
Creating targeted support programs to help small businesses absorb or mitigate increases in costs can alleviate some of the upfront setbacks. Financial support, tax incentives, or innovation grants might be instrumental in smoothing out this transition.
-
Dialogue with Trade Partners:
An active dialogue with international trade partners can help preempt retaliatory measures and foster a mutually beneficial trading environment. By engaging with allies and even those with conflicting interests, there is potential to mitigate a full-scale trade war.
Policymaker Proposals and the Push for a Balanced Approach
Some experts have suggested that a more nuanced approach could deliver both protection and global cooperation. Such strategies could include:
- Tiered tariff systems that gradually phase in increases for certain products based on specific conditions and industry benchmarks.
- Incentives for domestic companies that invest in green technologies or in re-training workers in heavily affected industries, ensuring that the industrial base remains competitive in an evolving marketplace.
- Collaborative research and development initiatives aimed at reducing the material intensity of industries reliant on steel and aluminum.
These proposals aim to address the fine points of tariff policy—that is, the underlying reasons for imposing such measures and their hidden complexities. With international pressure and domestic economic considerations shaping the debate, it becomes evident that a one-size-fits-all approach rarely suffices.
Balancing Domestic Interests with Global Responsibilities
Ultimately, the decision to expand tariffs on steel and aluminum products is indicative of a broader trend in which national interests are weighed against the demands of global markets. While the government’s intent is to safeguard domestic industries, the ripple effects across various sectors cannot be underestimated. In today’s interconnected world, small shifts in policy can lead to widespread adjustments in production, pricing, and even global trade dynamics.
Both businesses and policymakers must work through the off-putting challenges presented by these changes while keeping an eye on broader economic trends. Putting the right kind of support in place for small businesses, ensuring open channels of communication with global partners, and fostering an environment that balances competition with collaboration are key to finding lasting solutions.
Prioritizing Stability in a Turbulent Economic Environment
For manufacturers and businesses facing the new tariff measures, the following strategies might offer some stability in a period of adjustment:
-
Invest in Alternative Materials:
Where viable, companies might explore the use of substitute materials that are not subject to the extended tariffs. While this change may be nerve-racking initially, a diversified material base can improve long-term resilience.
-
Strengthen Domestic Partnerships:
Increased collaboration with local suppliers and manufacturers can help build a robust domestic supply chain that is less vulnerable to international trade tensions.
-
Adopt Advanced Technologies:
Investments in technology and automation can help offset rising labor and material costs, ensuring that production remains efficient despite higher input costs.
Conclusion: Toward a More Equitable Trade Future
In conclusion, the expansion of 50% tariffs on steel and aluminum products to include an additional 407 items continues to serve as a litmus test for US trade policy and the balancing act between domestic protection and international free trade. While the measure is designed to close loopholes, support foundational industries, and safeguard jobs at home, it also sets in motion a series of economic adjustments that stakeholders in industries as diverse as automotive, industrial manufacturing, and small business operations must navigate.
As we take a closer look at the new rules and their effects, it becomes crucial for policymakers, industry leaders, and business owners to work together in addressing the tricky parts, the tangled issues, and the subtle details that define this evolving trade landscape. A balanced approach—one that smoothed out the nerve-racking changes while nurturing innovation and open international dialogue—must be the way forward.
It is my view that, in navigating these headwinds, America can chart a path that protects its economic interests without compromising the broader commitment to global trade norms and responsible industrial practices. The coming months and years will be critical in assessing whether the intended outcomes of these tariff expansions materialize as hoped.
For those who are directly impacted, whether in the small business community or on the factory floors of major manufacturing plants, the challenge is clear: adapt, innovate, and work through the confusing bits of the current trade environment. With the right mix of strategic policy adjustments and industry initiatives, we can create an ecosystem that not only survives these turbulent times but flourishes in a balanced, competitive global market.
While the tariff expansion might seem like another complicated piece in the modern trade puzzle, it also offers an opportunity for introspection, innovation, and growth. Whether viewed as a protective measure or a risky escalation, one thing remains certain: in our interconnected world, the economic actions of one nation reverberate far beyond its borders. Maintaining open channels of dialogue, fostering resilience in supply chains, and prioritizing long-term stability over short-term gains will be essential strategies in making your way through these challenging times.
By staying informed, agile, and responsive to market signals, businesses small and large can seize the opportunities that emerge even in a policy landscape loaded with issues. The current debate over tariffs is a stark reminder of the delicate balance between domestic priorities and global economic realities—a balance that must be managed thoughtfully as we move toward a more equitable trade future.
Originally Post From https://mexicobusiness.news/mining/news/trump-expands-50-steel-aluminum-tariffs-407-more-productsa?tag=mining
Read more about this topic at
US Department of Commerce
Trump expands 50% tariff on steel and aluminum to 400 …